The Federal Tax Authority UAE made a significant public announcement on November 6, 2024. This greatly impacts businesses across the country. According to the decision, the FTA has granted a grace period for updating tax records. The announcement offers much-needed relief to businesses.
Those who face challenges with maintaining accurate tax data. The grace period extends from January 1, 2024, to March 31, 2025. Businesses will not be subject to administrative penalties during this duration. The ones failing to update their tax records as required.
The decision welcomes development for taxpayers. They are now free from additional burdens. As previously encountered difficulties with the FTA’s system limitations. A chance for them to avoid technical challenges in amending their records. Note that this grace period does not apply to late corporate income tax (CIT) registrations. It remains subject to penalties.
The blog explores the:
- Implications of this update
- The details surrounding it
- The actions businesses should take
These help businesses ensure compliance with UAE tax regulations.
What Does This Grace Period Mean for Businesses?
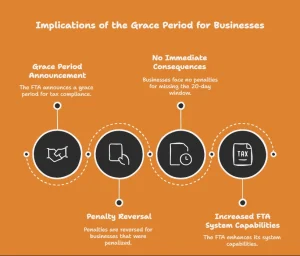
This relief phase allows businesses to update their tax records with the FTA without facing administrative fines. It gives room for error correction and allows the system to support updates with minimal technical disruptions. Business owners across industries can use this time to ensure their FTA profile reflects current and accurate information.
During this window, businesses will not face penalties for failure to notify the FTA about relevant changes. Previously, these penalties could range from AED 1,000 to AED 10,000, depending on the type and nature of the omitted update.
The penalties, if already imposed between January 1, 2024, and March 31, 2025, will be automatically canceled. If they were paid, they will be reversed and added back to the business’s tax account. This reversal can provide significant cash flow relief for small and medium enterprises.
Additionally, the current timeframe provides five extra months for businesses to act. It enables tax departments and accountants to gather necessary information and submit it to the FTA with full accuracy.
The UAE tax records update grace period can also be seen as a bridge to transition into a more efficient digital system. As the FTA improves its platform, businesses can benefit from more intuitive and accurate filing and record-update capabilities.
Key Aspects of the Cabinet Decision on Tax Records
The recent Cabinet Decision outlines the exact obligations of taxpayers when there are changes in their business details. The FTA’s public clarification in document TAXP007 makes these responsibilities clear.
The required updates include:
- Business name
- Registered office address
- Primary email contact
- Trade license or activity amendments
- Legal entity type
- Sector or operational nature
- Business location
Companies must notify the FTA within 20 business days of any changes to these areas. This notification is vital to remain compliant with current tax laws.
If this notification is not completed, penalties will apply. These can be financially damaging, especially for businesses undergoing multiple administrative changes.
Fortunately, this temporary relief allows businesses to catch up. They can align their tax records with actual operations and remove discrepancies accumulated over time.
This grace period in the UAE serves as a compliance reset opportunity, giving taxpayers the freedom to act without fear of financial punishment.
Implications of the Grace Period for Your Business
First, audit all existing data submitted to the FTA. Ensure the company’s registered name, physical address, and business activity are current. Confirm that your legal structure and primary communication channels are updated.
First, audit all existing data submitted to the FTA. Ensure the company’s registered name, physical address, and business activity are current. Confirm that your legal structure and primary communication channels are updated.
Next, identify issues. These may include system timeouts, portal errors, or inability to access specific sections. Save screenshots and error logs whenever possible for documentation.
Once you’ve identified obstacles, communicate them to the FTA. Submit all relevant error messages, screenshots, or support references via email. This proactive step can aid your case if penalties appear despite eligibility for reversal.
Start checking your tax account regularly. Log in and verify whether any previously applied fines have been canceled. If not, contact the authority for further clarification and request an adjustment where needed.
Keep your documentation complete. All emails, logs, portal screenshots, and FTA responses should be saved. These will form a strong audit trail if you face disputes or issues in the future.
This structured approach will ensure compliance during the grace period while also minimizing the risk of unresolved penalties in the long term.
When Does This Grace Period End?
The tax record update window spans from January 1, 2024, to March 31, 2025. This long timeframe gives businesses the breathing room to prepare documents and update their information properly.
However, waiting until the last minute could be risky. System overloads or unexpected documentation issues might delay updates beyond the cutoff.
Proactively making changes now will avoid a last-minute rush. It also allows businesses to align with future expectations in digital compliance and transparency.
Understanding the grace period meaning in a tax compliance context is essential—it’s not just about delaying action, but using the extra time strategically to align with regulatory standards.
What’s Not Covered by the Grace Period?
The relief only applies to tax record updates, not corporate tax registration. If your business hasn’t registered for Corporate Income Tax (CIT), penalties will still apply.
The FTA will continue to issue administrative fines for late registration or non-compliance related to CIT requirements. This includes late filing or non-payment of tax dues.
Businesses must distinguish between general tax record maintenance and formal corporate tax registration procedures. While one enjoys a waiver window, the other remains fully enforceable.
This ensures clarity in managing priorities during the grace period, with a focus on updates only, not omissions in mandatory filings.
Final Recommendations for Businesses
Use this period strategically. Review and correct your tax data. Stay ahead of compliance issues to avoid last-minute fixes.
Work closely with your internal finance or compliance team. In case of uncertainty, consider hiring an expert. Whether it’s system updates or audit preparation, their guidance can save time and penalties.
Investing in Tax Planning can help avoid unexpected charges. It’s also a good time to evaluate your future filing methods and integrate reliable Tax Optimization tools or services.
Proactively updating records today means fewer risks tomorrow. Avoid unnecessary stress by making use of the extended timeline provided.
Conclusion:
In the UAE, the grace period for updating corporate tax records is a welcome move. It offers businesses the chance to clean up their tax profiles without penalties and helps them adjust to evolving tax systems.
Still, this relief isn’t forever. Use the extra time wisely and update your tax records well before the deadline.
Need help interpreting the grace period or navigating the update process? Let MBS Consultancy handle the entire process, so you can stay focused on what matters—growing your business.